DNSmap is open source software licensed under the GNU GPL v2 which allows you to retrieve the subdomains attached to a specific domain. It is mainly used during the phase of information gathering.
During this phase, a pentester must collect as much information as possible on the target: IP addressing, domain names, network protocols, phone number, email address, etc.
This tool allows it to discover all the subdomains associated with a given domain (for example from google.com, it is possible to discover mail.google.com, earth.google.com, sketchup.google.com, desktop .google.com, …). DNSmap is intended for security professionals and pentesters as well as website administrators.
Main features of DNSmap:
- Obtain all IP addresses (A records) associated with each subdomain
- Interrupt the bruteforcing process in case the target domain uses wildcards
- Ability to be able to run the tool without providing a list to do a bruteforce attack
- Save results in a readable format
Installing DNSMAP
DNSMAP only works under Linux, if you have a computer running Windows I advise you to use a virtual machine running the “Kali Linux” Linux distribution. Just download VMware and a Kali Linux image. DNSMAP is already pre-installed on it.
Otherwise to install it on another distribution, open a terminal as root and run the following commands:
#tar -zxvf dnsmap-0.30.tar.gz
#cd dnsmap-0.30
#make or #gcc -Wall dnsmap.c -o dnsmap
#cp ./dnsmap / usr / local / bin / dnsmap
#cp ./dnsmap-bulk.sh / usr / local / bin /
#chmod ugo + x /usr/local/bin/dnsmap-bulk.sh
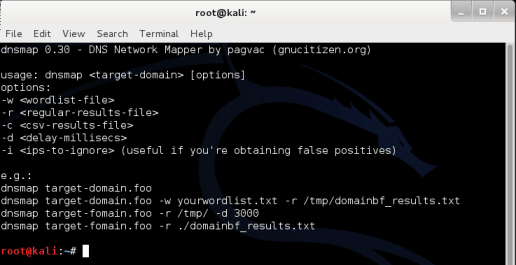
How to use DNSmap?
Basic syntax:
And here are the different options:
-W
Input file to use for brute force attack
-R
Export results in text format
-VS
Save files in csv format
-D
Maximum delay (in ms) between 2 DNS requests
(Default: 10 ms)
-I
It allows to ignore certain IP addresses when displaying the result (useful for domains generating false positives)
Practical case:
On a distribution like Kali Linux, DNSmap is accessible via the menu “Applications -> Kali Linux -> Information Gathering -> DNS Analysis -> dnsmap”
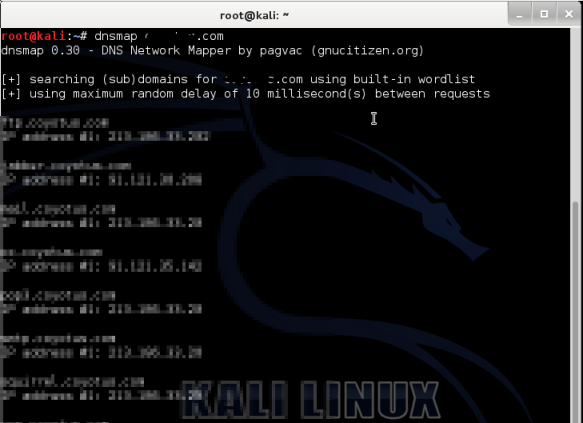
For ease of use, we'll run a Brute Force subdomains using the wordlist built into the tool. To do this, we type the following command:
To do a brute force subdomain attack using a different wordlist, we type this command:






Need help ? Ask your question, FunInformatique will answer you.